
Ref: A general reminder 1) The next tutorial will happen in, friday, 5.00 pm. Different mode of interaction happen at different energy scale (or length scale).In comparison, photoelectricity occurs at a much lower energy scale, ~ eV.

Note that Compton scattering occurs at energy scale which is much higher, ~ 0.1 MeV (typical energy of the x-ray photon, with the wavelength ~ Compton wavelength of the electron.In the limit l infinity (low incident photon energy), l > lc, Rayleigh scattering dominates (The effective mass is large as seen by the incident photons)
COMPTON EFFECT VIDEO FREE
This is just the Compton effect The unshifted peak corresponds to collision of photon with strongly bounded electron which is not free (incident photon energy > me) instead, such that Dl (due to Matom) > latom
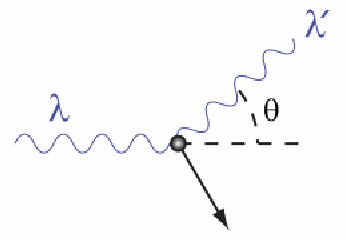
Find (a) the wave length of the scattered x-rays, (b) the energy of the scattered x-ray photons, (c) the kinetic energy of the scattered electrons, and (d) the direction of travel of the scattered electrons. X-rays of wavelength 0.2400 nm are Compton scattered and the scattered beam is observed at an angle of 60 degree relative to the incident beam. Dl= Dlmax = 2 lc =2( 0.00243nm) (photon being reversed in direction), Dl is maximum Dlmax 180o l’=0.1795 nm. Consider some limiting behaviour of the Compton shift: q0 Be reminded that the relationship is derived by assuming light behave like particle (photon)įor q = 00 “grazing” collision =>Dl = 0 l l’ l l l’= l+Dlmax Dl≡ l’- l= (h/mec)(1 - cosq) Notice that Dl depend on q only, not on the incident wavelength, l. The Compton scattering experiment can now be perfectly explained by the Compton shift relationship Dl≡ l’- l= le(1 - cosq) as a function of the photon scattered angle. Note that the wavelength of the x-ray used in the scattering is of the similar length scale to the Compton wavelength of electron. le = h/mec = 0.0243 Angstrom, is the Compton wavelength (for electron). Some algebra… Mom conservation in y: p’sinq = pesinf (PY) Mom conservation in y: pecosf= p - p’cosq (PX) Conservation of total relativistic energy: E + mec2 = E’ + Ee (RE) (PY)2+ (PX)2, substitute into (RE)2 to eliminate Ee and pe: (E + mec2 - E’)2 = c2(p2 – 2pp’cosq+p’2)+ mec2, leading to Dl≡ l’- l = (h/mec)(1 - cosq) P’sinq = pesinf p = p’cosq + pecosf Conservation of momentum in 2-D p = p’ + pe (vector sum) actually comprised of two equation for both conservation of momentum in x- and y- directions Conservation of l.mom in y-direction Conservation of l.mom in x-direction Scattered photon, E’=hc/l’, p’=h/l’ q f 1: Conservation of E: hc/l + mec2= hc/l’ + Ee Initial photon, E=hc/l, p=h/l Initial electron, at rest, Eei=mec2, pei=0 y x Scattered electron, Ee,pe 2: Conservation of momentum:p = p’ + pe (vector sum) For various angle q the scattered x-ray is measured as a function of their wavelength Unexplained by classical wave theory for radiation No shift of wavelength is predicted in wave theory of lightĬompton (and independently by Debye) explain this in terms of collision between collections of (particle-like) photon, each with energy E = hn, with the free electrons in the target graphite (imagine billard balls collision) Wavelength shift Beam of x-ray with sharp wavelength l falls on graphite target. The discovery of the Compton effect confirmed that electromagnetic radiation has both wave and particle properties, a central principle of quantum theory.Īlthough initially the incident beam consists of only a single well-defined wavelength (l) the scattered x-rays have intensity peaks at two wavelength (l’ in addition), where l’ > l. The Compton effect is the change in wavelength of high energy electromagnetic radiation when it scatters off electrons. Another experiment revealing the particle nature of X-ray (radiation, with wavelength ~ 10-10 nm) Compton, Arthur Holly (1892-1962), American physicist and Nobel laureate whose studies of X rays led to his discovery in 1922 of the so-called Compton effect.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
